-
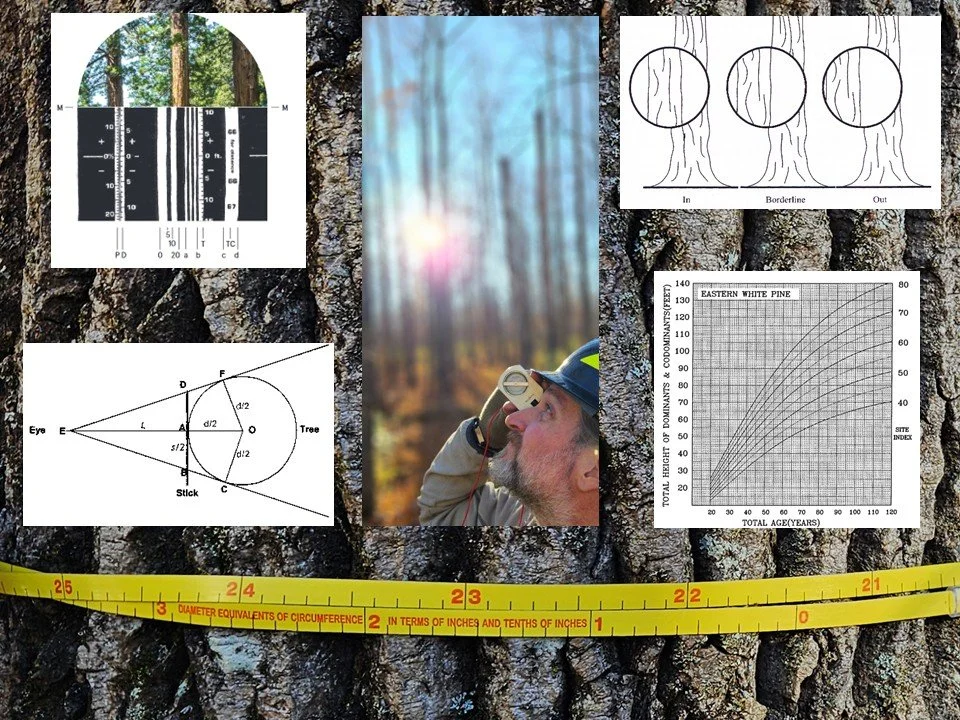
This course will give you the skills to help in planning, collecting, analyzing, and summarizing vegetation and habitat data for any purpose. In this course you will learn: (1) the importance of numerical and unit literacy and the variety to metrics we can use to quantify vegetation (such as Quadratic Mean Diameter, Basal Area, Density, Horizontal and Vertical Cover, Age and Size Distributions, Wood Volume, Biomass, and Primary Productivity); (2) techniques and tools for collecting and using spatial data and mapping vegetation; (3) techniques and tools for quantifying vegetation cover, density, deadwood/snags, and basal area; (4) techniques and tools to measure and scale individual trees to estimate individual and plot level metrics including volume and biomass; (5) variable radius sampling methods and sampling design. Throughout the course we will integrate data summary and analysis techniques for quantifying vegetation conditions/ structures/ trends.
-
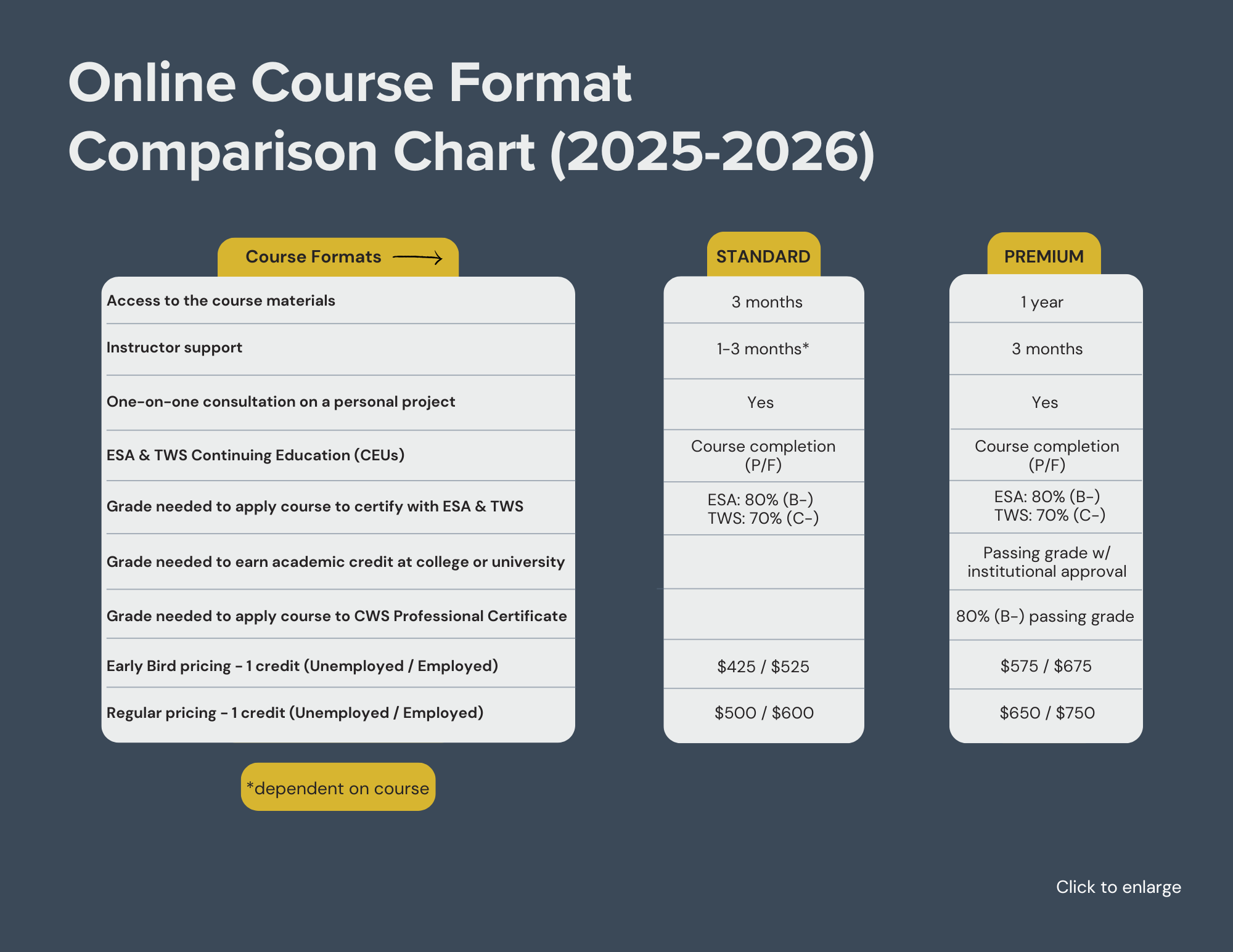
Learn at your own pace with instructor support (see Online Course Format Chart below for details).
Spring: March 2 – May 24, 2026 (Early bird* ends February 1)
*Early bird saves $75
-
Introductory statistics and basic experience using spreadsheets
-
Module 1: Why numbers matter: The basics of numerical literacy and vegetation metrics for research, monitoring, and management
Describe how numerical literacy applies to a project you are working on or have worked on
Evaluate the tradeoffs between collecting data at the coarse or fine scale
Describe how bias, uncertainty and errors related to a past or ongoing project
Define the tools used to measure lines, angles, presence, conditions, and locations
Define the vegetation metrics that are commonly used to communicate vegetation size, the abundance of vegetation, the stocking or “fullness”, the history of the vegetation, the abundance or location of vegetation structural components, the amount of forest products or biomass, and the growth or productivity of vegetation
Module 2: The basics of spatial data and plane surveying: How to collect robust data for locations, distances, horizontals angles, and areas
Record robust location data and understand sources of uncertainty
Make and use a simple field
Measure reliable and accurate horizontal angles with a compass
Calibrate your pacing for measuring distances in the field
Measure area of land or vegetation features
Module 3: Sampling vegetation with counts, transects, and fixed area plots: Combining presence/abundance/conditions with distances and areas
Estimate surface cover using Robel poles and % area coverage tools
Estimate vertical cover using densiometers
Quantify canopy layers and vegetation vertical structure
Estimate volume and mass of deadwood and fuel loads
Complete fixed area sampling for density estimates
Module 4: Measuring dimensions and ages of individual trees and shrubs, and scaling to estimate volume and mass
Measure diameter of woody vegetation in robust and repeatable ways
Quantify vegetation height and canopy properties using measurements of distance and angles
Scale individual tree measurements into estimates of tree volume
Calculate stand level estimates of size, density, basal area, volume and biomass
Estimate age of individuals by counting rings or annual height growth
Module 5: Simplifying sampling using variable radius methods, putting it all together to summarize the site, and planning the sampling for the next time we measure
Utilize variable radius sampling methods to sample forests
Scale stand level data from variable radius sampling
Use the previously covered measurement techniques to estimate growth/ productivity/ carbon sequestration
Demonstrate data summary methods for presenting information about forest conditions
Plan a sampling effort by matching needs with sampling designs
COURSE OPTIONS & INFORMATION (Review chart above, then click below)
-
FORMAT:
3 months of access to course materials as you work at your own pace
Get instructor support for the 3-month term via email, discussion threads, group meetings, and one-on-one appointments
After working through the course materials, set up an optional meeting with the instructor to discuss your own personal project from work or school
CONTINUING EDUCATION:
16 CEUs with The Wildlife Society
CERTIFICATIONS:
Earn 1 credit toward certification as an Associate/Certified Wildlife Biologist® (at any level) with The Wildlife Society
-
FORMAT:
12 months of access to course materials as you work at your own pace
Get instructor support for the 3-month term via email, discussion threads, group meetings, and one-on-one appointments
After working through the course materials, set up an optional meeting with the instructor to discuss your own personal project from work or school
CONTINUING EDUCATION:
16 CEUs with The Wildlife Society
Go to our Continuing Education Page for more details
CERTIFICATIONS:
Earn 1 credit toward certification as an Associate/Certified Wildlife Biologist® (at any level) with The Wildlife Society
ACADEMIC CREDIT:
Earn 1 academic credit (go to our Academic Credit Page for details)
Earn an additional 1-2 academic credits with an Applied Project
INSTRUCTOR:
SCHOLARSHIPS
Full scholarships are available to participants from countries designated as “lower income” and “lower middle income” in the World Bank List of Economies. Please see our CWS World Scholars Program page for details.
CANCELLATION POLICY
Cancellations 30 days or more before the start date are not subject to cancellation fees. Cancellations <30 days before the start date are subject to a 50% cancellation fee. No refunds once the course begins.